Geo-SMART
Global Earth Observation and AI-enabled Scalable MApping and Decision-Relevant Water Assessment Tool


Geo-SMART: AI-powered, high-resolution mapping of global groundwater and terrestrial water storage for smarter, data-driven water management.
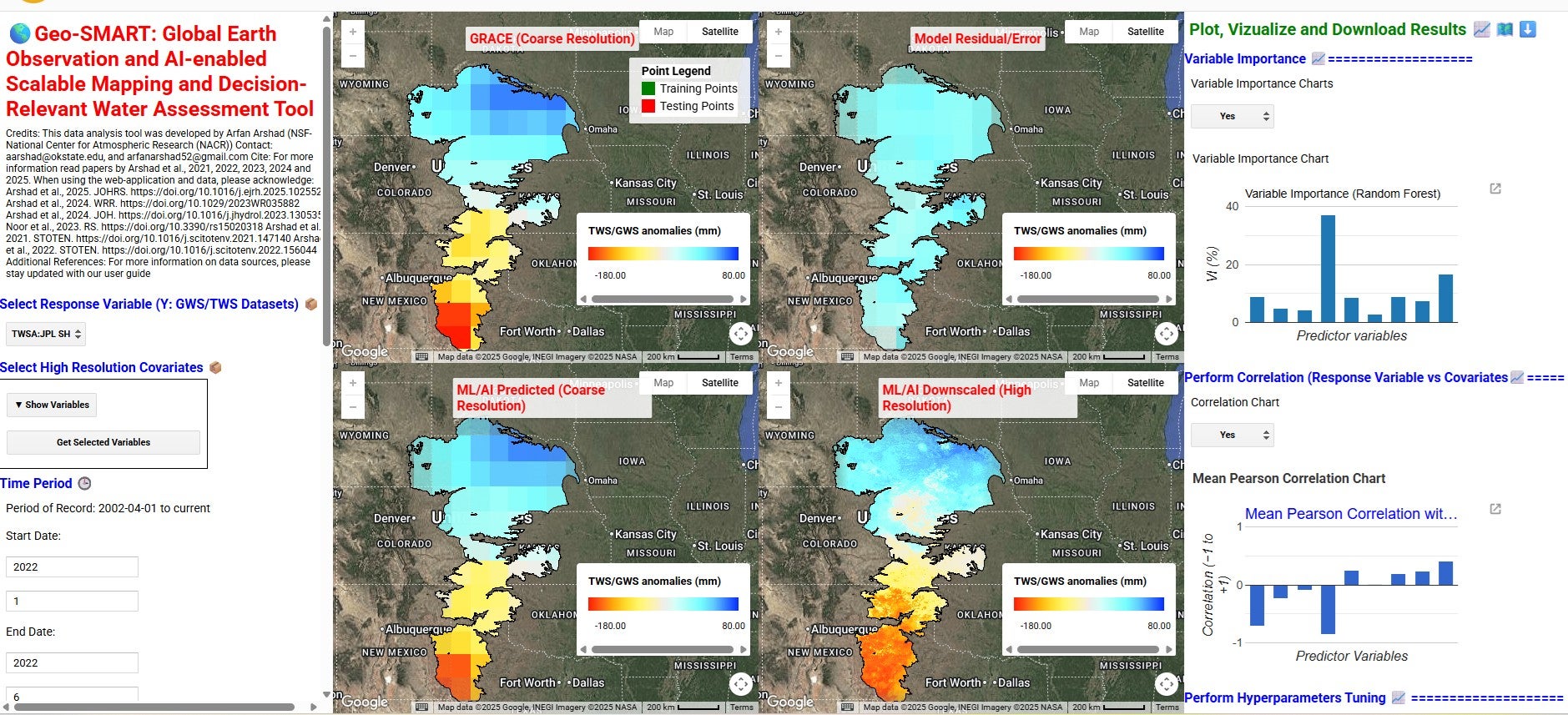
Snap view of GEO-SMART UGI.
GRACE (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) and its Follow-On mission (GRACE-FO) data are widely used for monitoring terrestrial and groundwater storage (TWS/GWS) variations across the globe. However, the coarse resolution (~27 km to 111 km) of post-processed GRACE datasets remains inadequate for decision-relevant assessment of terrestrial and groundwater resources. Machine learning (ML) and AI-driven spatial downscaling have gained more attention to improve the resolution of remote sensing products, enabling them particularly suitable for local decision-making and effective water resource management. The computationally intensive task of acquiring data from various sources and postprocessing them for input into ML/AI models puts these out of the reach of many researchers and practitioners.
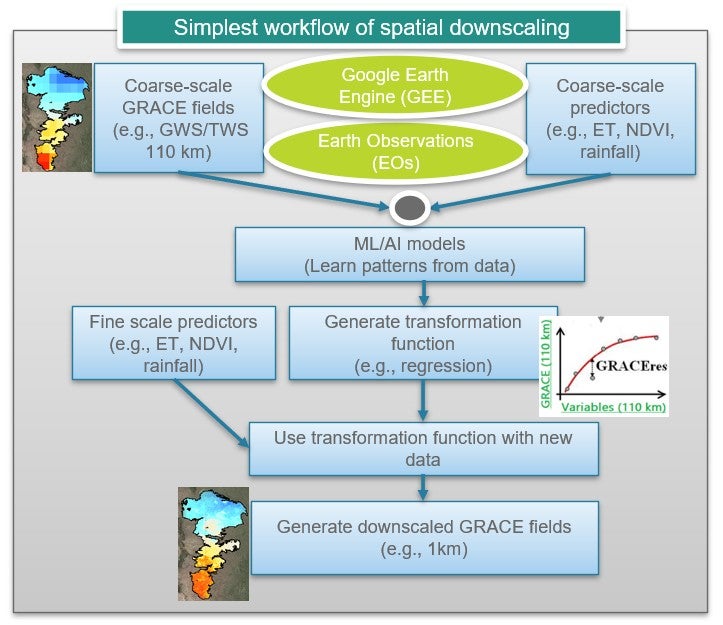
Workflow of spatial downscaling using ML/AI models.
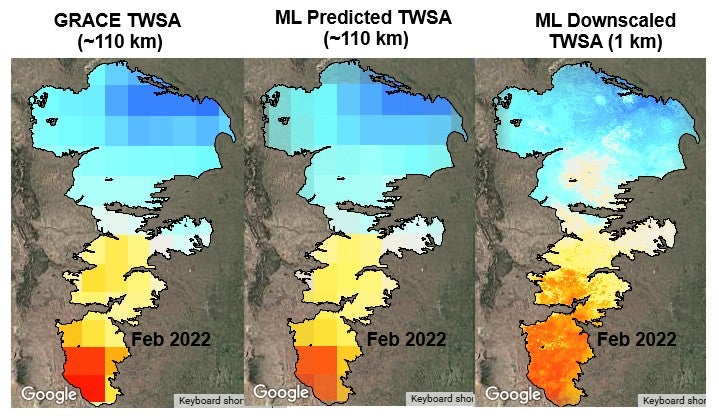
Comparison of GRACE TWSA with ML predicted and downscale results.
To solve this challenge, we developed the Global Earth Observation and AI-enabled Scalable Mapping and Decision-Relevant Water Assessment Tool (Geo-SMART). Geo-SMART is a web-interface downscaling tool that streamlines planetary-scale data of GRACE and Earth Observations (EOs) variables via Google Earth Engine. It provides TWS data from multiple GRACE products. By integrating snow water, soil moisture and canopy water storage from multiple data sources (e.g., FLDAS, GLDAS, and ERA5-Land), web-tool supports groundwater storage (GWS) estimation. Geo-SMART use different ML/AI models (e.g., random forest, support vector machine, regression trees, gradient boosting trees) which learn the downscaling function of coarse-scale GRACE data given high-resolution EOs fields (e.g., vegetation, land surface temperature, soil moisture, snow, rainfall, elevation and evapotranspiration), mapping coarse-scale GRACE to high-resolution field. It first uses the ML/AI trainings algorithms between coarse-scale GRACE and EOs, followed by a super-resolution testing step to generate high-resolution fields of TWS and GWS from GRACE. Geo-SMART framework consists of wide range of functionalities according to user’s needs. These include selection of their own area of interest, developing local model, calibrate model parameters and optimizing them, checking model performance on training and testing data, derived downscaled map at any scalable resolutions (kilometers to meters) and visualizing spatial maps from 2002 to the present. In addition, Geo-SMART also provides users with downloading the results and raw data used in model training and testing development to develop their own external models (e.g., ANN) that do not exist in the tool. Geo-SMART lowers technical barriers and enables water managers, policymakers, and stakeholders to incorporate satellite-driven, decision-relevant insights into sustainable water resources planning and management.
Geo-SMART with Other Custom Programming Environments

Geo-SMART also enables users to prepare and export both coarse-scale GRACE fields and high-resolution Earth Observation (EO) variables—such as vegetation, land surface temperature, soil moisture, snow, precipitation, elevation, and evapotranspiration—at any user-defined resolution.
These datasets can serve as inputs to any other programming environment (e.g., R and Python), allowing users to perform independent downscaling experiments using their custom AI/ML models.
The coupled Geo-SMART + RStudio framework allows users to:
- Download and preprocess variables from the Geo-SMART web tool.
- Use R scripts to clean, merge, and format the data for machine-learning workflows.
- Apply diverse ML/AI models—including Random Forest (RF), Geographically Weighted Random Forest (RF-GW), XGBoost, CART, SVM, and ANN—for customized downscaling and analysis.
Comprehensive R scripts, sample datasets, and step-by-step instructions are available on GitHub.
https://github.com/arfan1994/GeoSMART-and-Rstudio-Based-Spatial-Downscaling
Geo-SMART Development Team
- Arfan Arshad, NSF NCAR Research Applications Laboratory
- Cenlin He, NSF NCAR Research Applications Laboratory
- Ali Mirchi, Oklahoma State University
Resources
-
Multi-model ensemble machine learning-based downscaling and projection of GRACE data reveals groundwater decline in Saudi Arabia throughout the 21st century
Description
Arshad, Arfan, Muhammad Shafeeque, Thanh Nhan Duc Tran, Ali Mirchi, Zaichen Xiang, Cenlin He, Amir AghaKouchak, Jessica Besnier, and Md Masudur Rahman. "Multi-model ensemble machine learning-based downscaling and projection of GRACE data reveals groundwater decline in Saudi Arabia throughout the 21st century." Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 60 (2025): 102552.
-
Downscaled‐GRACE data reveal anthropogenic and climate‐induced water storage decline across the Indus Basin
Description
Arshad, A., Mirchi, A., Taghvaeian, S., & AghaKouchak, A. (2024). Downscaled‐GRACE data reveal anthropogenic and climate‐induced water storage decline across the Indus Basin. Water Resources Research, 60(7), e2023WR035882.
-
Combining downscaled-GRACE data with SWAT to improve the estimation of groundwater storage and depletion variations in the Irrigated Indus Basin (IIB)
Description
Arshad, Arfan, Ali Mirchi, Maryam Samimi, and Bashir Ahmad. "Combining downscaled-GRACE data with SWAT to improve the estimation of groundwater storage and depletion variations in the Irrigated Indus Basin (IIB)." Science of the Total Environment 838 (2022): 156044.
-
Reconstructing high-resolution groundwater level data using a hybrid random forest model to quantify distributed groundwater changes in the Indus Basin
Description
Arshad, Arfan, Ali Mirchi, Javier Vilcaez, Muhammad Umar Akbar, and Kaveh Madani. "Reconstructing high-resolution groundwater level data using a hybrid random forest model to quantify distributed groundwater changes in the Indus Basin." Journal of Hydrology 628 (2024): 130535.
-
Combining APHRODITE Rain Gauges-Based Precipitation with Downscaled-TRMM Data to Translate High-Resolution Precipitation Estimates in the Indus Basin
Description
Noor, Rabeea, Arfan Arshad, Muhammad Shafeeque, Jinping Liu, Azhar Baig, Shoaib Ali, Aarish Maqsood et al. "Combining APHRODITE Rain Gauges-Based Precipitation with Downscaled-TRMM Data to Translate High-Resolution Precipitation Estimates in the Indus Basin." Remote Sensing 15, no. 2 (2023): 318.
-
Reconstructing high-resolution gridded precipitation data using an improved downscaling approach over the high altitude mountain regions of Upper Indus Basin (UIB)
Description
Arshad, Arfan, Wanchang Zhang, Zhijie Zhang, Shuhang Wang, Bo Zhang, Muhammad Jehanzeb Masud Cheema, and Masoud Jafari Shalamzari. "Reconstructing high-resolution gridded precipitation data using an improved downscaling approach over the high altitude mountain regions of Upper Indus Basin (UIB)." Science of the Total Environment 784 (2021): 147140.